EUR 2.6 million in REACT-EU recovery assistance:
New imaging device network advances research

The confocal laser scanning microscope (Zeiss LSM 980) enables the examination of cell structures and whole cells as well as live cell analysis. | Image source: University of Hohenheim / Oliver Reuther
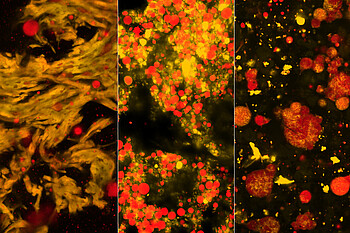
Milk-based mozzarella (l.) compared to almond-based (m.) and rice-based (r.) mozzarella-like cheese analogs stained with Rhodamine-B (yellow = protein) and Fat Red (red = fat) (imaged with Zeiss LSM 900). | Image source: University of Hohenheim / Sandra Ebert

Researchers at the Core Facility Hohenheim (CFH) discuss an image taken with the confocal super resolution microscope (ZEISS LSM 980). | Image source: University of Hohenheim / Oliver Reuther
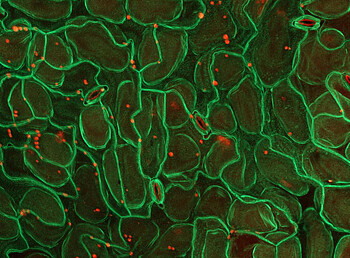
Plant proteins made visible: The adhesion molecules on the cell membrane mediate contact and enable communication between the cells (imaged with ZEISS LSM 980). | Image source: University of Hohenheim / Tatsiana Straub, Lin Xi

The isotope ratio mass spectrometer (IRMS) is used to classify the results from the imaging techniques: In particular, the isotope ratio can be used to reconstruct the origin of nutrients from the soil, create fluxes of substances within plants, and quantify the interaction of plants with insects. | Image source: University of Hohenheim / Oliver Reuther

Head of a bee imaged with the environmental scanning electron microscope (Zeiss EVO15). | Image source: University of Hohenheim / Susanne Karck

The correlative Raman atomic force microscope (WITec alpha300) can be used to study the surface structures and chemical composition, e.g. of living organisms or food. | Image source: University of Hohenheim / Oliver Reuther
